What do you want to do?
Text search queries let you search for words or phrases in your sources. You can choose to search only the textual content of your sources, only in annotations or both.
You can select the source content you want to search, by selecting sources, nodes, sets, folders or search folders.
Before you run a Text Search query, make sure the text search language is set to the language of your source materials—refer to Set the text search language and stop words for more information.
You can use a Text Search query to:
Explore the use, context and meaning of words—are some expressions used more widely in a specific demographic?
See if an idea or topic is prevalent in your sources—particularly in the early stages of your project.
Locate an annotation that you remember writing.
Automatically code words or phrases. For example, find each occurrence of solar or wind power and code them (and the selected context around them) at the node renewable energy. Refer to Broad brush coding using queries for more information.
You can search for exact words, phrases or even concepts that include similar words. For example, if you search for sport, NVivo can find words with similar meanings: recreation, play, and fun.
You can use a Compound Query to further refine a text search, for example you could
NOTE You cannot use Text Search queries to search for words or phrases in framework matrix summaries.
On the Explore tab, in the Queries group, click New Query, and then click Text Search.
The Text Search Query dialog box opens.
On the Text Search Criteria tab, in the Search for box, enter the word or phrase. If you want an exact phrase enclose it in double quotation marks (").
(Optional) Adjust the Finding matches slider to find words or phrases with a similar meaning. By default, the slider is set to find 'Exact match only'—refer to Understand text match settings for more information.
(Optional) Click Special to combine multiple words with special characters and operators.
In the Search in box, select whether you want to search in Text, Annotations or both.
To change the scope of the query:
In the Of box, select which project items you want to include in the search—click the Select button to select the project items.
In the Where box, choose to include only project items created by selected users—click the Select button to select the users.
(Optional) Click the Query Options tab to save the results in a node or set, and to define the spread coding options (amount of coding spread around the search word). By default, only the word or phrase is coded—to make references more meaningful, you may want to increase the spread. Refer to Spread coding for more information.
Click Run.
NOTE
To save the Text Search query, select the Add to Project check box and enter the name and description (optional) in the General tab.
By default, spread coding is set to 'None'. If you choose to spread coding, you cannot view the results as a word tree.
PDFs created by scanning paper documents may contain only images—each page is a single image. You cannot query text within images. If you want to use Text Search queries to explore the text in these PDFs, then you should consider using optical character recognition (OCR) to convert the scanned images to text (before you import the PDF files into NVivo).
For more information about saving queries, refer to Specify save options during query set up.
When you run a Text Search query, by default, the Summary tab is in focus showing a list of all sources that contain the word or phrase.
Click the other tabs on the right to see:
Reference The results are opened as a node preview and the word or phrase is shown with a narrow context. You can also expand the context around a reference.
Text, Picture, Audio, Video, or Dataset Displays the results found in each type of source—only relevant tabs are available.
Word Tree Displays the results as a tree with branches representing the various contexts in which the word or phrase occurs. You may be able to find recurring themes or phrases that surround the word. The size of the font indicates the number of times the word or phrase was found. The Word Tree tab is not available when you select to spread coding.
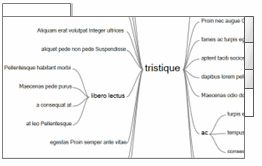
When you view the results as a Word Tree, you can:
Click a branch to highlight all of the other related branches to see the wider context.
Change the number of words that are displayed in the branches— in the Context (Words) box, in the Options group on the Word Tree tab, select the number of words you want to show.
Change the order of the branches in the word tree. In the Branch Order box, in the Options group, on the Word Tree tab, select Alphabetical (to order branches alphabetically), or Number of matches (to order branches by the frequency in which the branch occurs).
Display a different word as the root. For example, if you search for contaminate including stemmed words and synonyms, you may find that pollution is at the root of the branches because it occurs more frequently. To select a different root word, in the Root Term box, in the Options group, on the Word Tree tab, select the root term you want to show.
Find the project item where a particular occurrence of the word is used—right-click on a branch to see the short-cut menu, then click Run Text Search Query.
You can use a Text Search query to find and code specific words or phrases. For example, you can search for the word policies and store the results at the node government.
Create the Text Search query and define the criteria—refer to Run a Text Search Query.
In the Text Search Query dialog box, click the Query Options tab.
Under Results, in the Options list, select Create Results as New Node.
By default, the new node will be stored in the Results folder—to change the location click the Select button next to the Location box.
In the Name box, enter a name for the new node.
(Optional) Enter a description of the new node.
Under Spread Coding, in the Spread to list, select the amount of context you want to code. By default, only the word or phrase is coded—to make references more meaningful, you may want to increase the spread. Refer to Spread coding for more information.
Click Run to find and code the specified text.
The result node is displayed in Detail View, each reference is displayed with the coded content in black and the context in grey.
NOTE
When you store a node in the Results folder it remains linked to the query that generated it—on the Home tab, in the Item group, click Open, and then click Open Linked Query. If you choose to store it in another location, the link is broken.
If you choose to Create Results as New Node Hierarchy, aggregation is turned on by default. To turn off aggregation, clear the Aggregate check box.
When running a Text Search query, NVivo applies the following rules:
In audio and video transcripts, only words in the Content field (column) are included in the query—any words in custom transcript fields are ignored.
In datasets, only words in codable fields (columns) are included in the query—any words in classifying fields are ignored.
A Text Search query does not find the 'stop words' associated with the text search language, unless the stop word is contained within a search phrase. Stop words are less significant words, such as conjunctions and prepositions. You can edit the list of stop words to suit the content of your sources—refer to Set the text search language and stop words for more information.
A Text Search query does not find parts of words, symbols, or punctuation.
You can adjust the Finding matches slider to find words with the same stem or words with similar meaning—for example, you can search for sport and find sport, sporting, play and basketball. Refer to Understand text match settings for more information.
TIPS
If you search for individual words, you will find only individual words—not phrases. For example, if you search for unemployed and adjust the Finding matches slider to find similar words, you will find unemployment and jobless, but not out of work.
You may be able to find similar words if you search for a phrase—depending on the phrase . For example, if you search for words similar to "out of work", you will find any instances of unemployed and jobless.
If you search for a combination of a single word and a phrase (for example, "out of work" OR unemployed), you will not be able to find similar words.
If you search for a phrase, the results will not include words with the same stem. For example, if you search for "alternative energy", you will not be able find "alternative energies".
If you include the special search operator 'tilde' (~) to specify proximity in your Text Search Criteria, the results will not include words with the same stem.
If you include the special search operators 'wildcard' (*) and 'fuzzy' (~) in your Text Search Criteria, you will be limited to 'Exact match only'.
If a word has multiple meanings, you may get unexpected results—refer to When I look for similar words, I get words I did not expect for more information.