This topic will get you started with coding audio and video sources—refer to More manual coding techniques and Automatic coding in audio and video sources for more detailed information.
What do you want to do?
In audio and video sources you can code:
A section of the media via the timeline
Text in the Content field (column) of a transcript (if you have one)

NOTE You cannot code text inside custom fields (columns), but you can use custom fields to auto code the whole transcript. Refer to Automatic coding in audio and video sources for more information.
On the timeline, click and drag to select the timespan that you want to code. You can also code text in the Content column of the transcript.
NOTE You can hide the waveform to make selection on the timeline easier— on the Media tab in the View group, clear the Waveform check box.
On the Analyze tab, in the Coding group, under Code Selection At, click New Node.
The New Node dialog box is displayed.
(Optional) To choose where you want to store the node—in the Location box, click the Select button and select the location.
Enter a name for the node.
(Optional) Enter a description of the node.
Click OK.
NOTE If you want to code at a node that already exists, click Existing Nodes, under Code Selection At, and select the relevant node.
Refer to More manual coding techniques for more detailed information about coding.
To see what has been coded in your audio or video source:
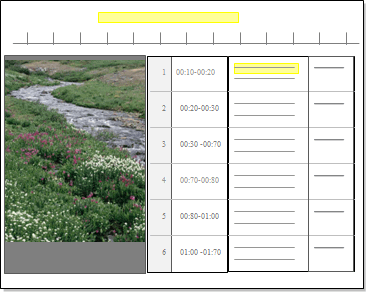
Turn on coding highlight - on the View tab in the Coding group, click the arrow next to Highlight, and then select a highlight option. A yellow bar is displayed above the timeline or in the transcript to indicate coding:
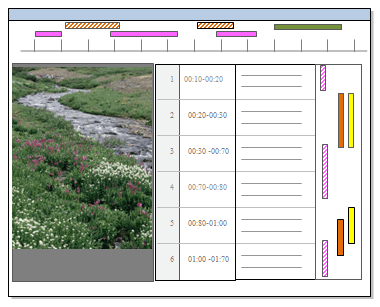
Turn on coding stripes— on the View tab in the Coding group, click the arrow next to Coding Stripes, and then select an option. Coding stripes for the media are displayed above the timeline and coding stripes for the transcript are displayed on the right:
For more detailed information on coding highlight and coding stripes— refer to Highlight coding or display coding stripes.
When you code a portion of the timeline, the associated transcript text is also indirectly coded, this is called 'shadow coding'. Similarly if you code the transcript, the associated section of the media is shadow coded. This is a quick way of determining which part of the timeline the coded transcript refers to and vice-versa.
Shadow coding saves you from having to code both the media and associated transcript content. For example, if you coded the transcript entry, you do not have to code the associated audio/video timeline—when you open the node, you can see the timeline that has been shadow coded.
You can distinguish the shadow coding stripes from the normal coding stripes by its pattern. The example below indicates that the main coding was done on the transcript and the timeline is shadow coded:
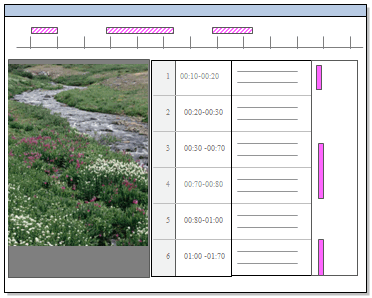
NOTE If you coded the timeline directly, the transcript will still be shadow coded but it will not be shown in the node.
When you are reviewing the coding stripes for the audio or video source, you can turn the shadow coding on or off.
On the View tab, in the Coding group, select or clear the Shadow Coding check box.
Shadow coding in the open source is turned on/off.
NOTE By default, shadow coding is always turned on when you first open an audio or video source and display coding stripes.
Select the node in List View.
On the Home tab, in the Item group, click Open.
The node opens in Detail View.
Click on the Audio or Video tab.
NOTE You can also open nodes from the main coding stripes or the shadow coding stripes—right-click on the coding stripes to display the shortcut menu, and then click Open Node.