Narrow, broad and custom reach settings
What do you want to do?
Use reach settings to see more context in a node
When you explore coding references in a node, you can choose to see more or less of the original source context—on the View tab, in the Detail View group, click Node and then choose a coding context.
This table shows the context (displayed in light grey) around coding references for the various types of source content:
|
Source content
|
Example
|
|
Coded text—in documents, PDFs, memos, externals, audio/video transcripts, picture logs and datasets.
|
I feel very worried about climate change, especially the impact on my children. We live on the coast so I am particularly concerned about rising sea levels and the destruction of the beautiful coral reefs. The problems seem overwhelming and I don't know where to start.
|
|
Coded audio or video content.
|
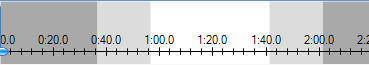
|
|
Coded regions of a picture or PDF page.
|

|
Using reach settings, you can choose how much context you want to see. For example, you can choose
-
Narrow to see 5 words, 5 seconds or 5 percent on either side of the coding reference
-
Broad to see the surrounding paragraph/cell, 20 seconds or 20 percent on either side of the coding reference
-
Custom to define specific reach settings
Reach settings vary depending on the type of source you are working with. For example, if you are working with a video the reach setting is measured in duration (seconds) while in a picture it is measured as a percentage of the picture.
You can also use reach settings to spread coding to the context.
You can change the defaults for narrow and broad reach settings in Application Options.
 Top of Page
Top of Page
Use reach settings to define proximity in queries
You can use Coding, Compound or Matrix Coding queries to combine query criteria. For example, you could gather content coded at coral bleaching where it is NEAR content coded at rising sea temperatures. To specify how proximity is measured you can use the narrow, broad and custom reach settings:
-
In Narrow Context within 5 words, 5 seconds or 5 percent.
-
In Broad Context within the surrounding paragraph/cell/row, 20 seconds or 20 percent.
-
In Custom Context define specific number of words, surrounding cell/row, duration or percentage.
Reach settings vary depending on the type of source you are working with. For example, in a video you may want to gather the content coded at erosion where it occurs within 20 seconds of content coded at coastal degradation.While in a dataset you may want to gather content coded at erosion where it occurs in the same cell or row as coastal degradation.
 Top of Page
Top of Page
Use reach settings to define spread coding options in queries
When you setup a Text Search, Coding or Compound query you can save the gathered content in a node. You can choose to spread the coding to include more of the context around each coding reference—for example, you could run a Text Search query to find and code the term solar power, including the paragraph around it (broad context). You can choose:
-
Narrow Context to code 5 words, 5 seconds or 5 percent on either side of the matched content.
-
Broad Context to code the surrounding paragraph/cell, 20 seconds or 20 percent on either side of the matched content.
-
Custom Context to code a specific amount of context around matched content.
Reach settings vary depending on the type of source included in the query scope. For example, you could query audio sources to gather content coded at salinity and pollution and gather it into a new node called water quality. You could spread the coding to include 20 seconds duration around each coding reference.
 Top of Page
Top of Page
Change the default reach settings
To change the default settings for narrow and broad reach settings:
-
Click the File tab, and then click Options.
-
On the General tab, under Context/Spread/Proximity, click Narrow or Broad.
-
Move through the tabs and define the default settings for each type of source.
-
Click OK.
 Top of Page
Top of Page
Related Topics